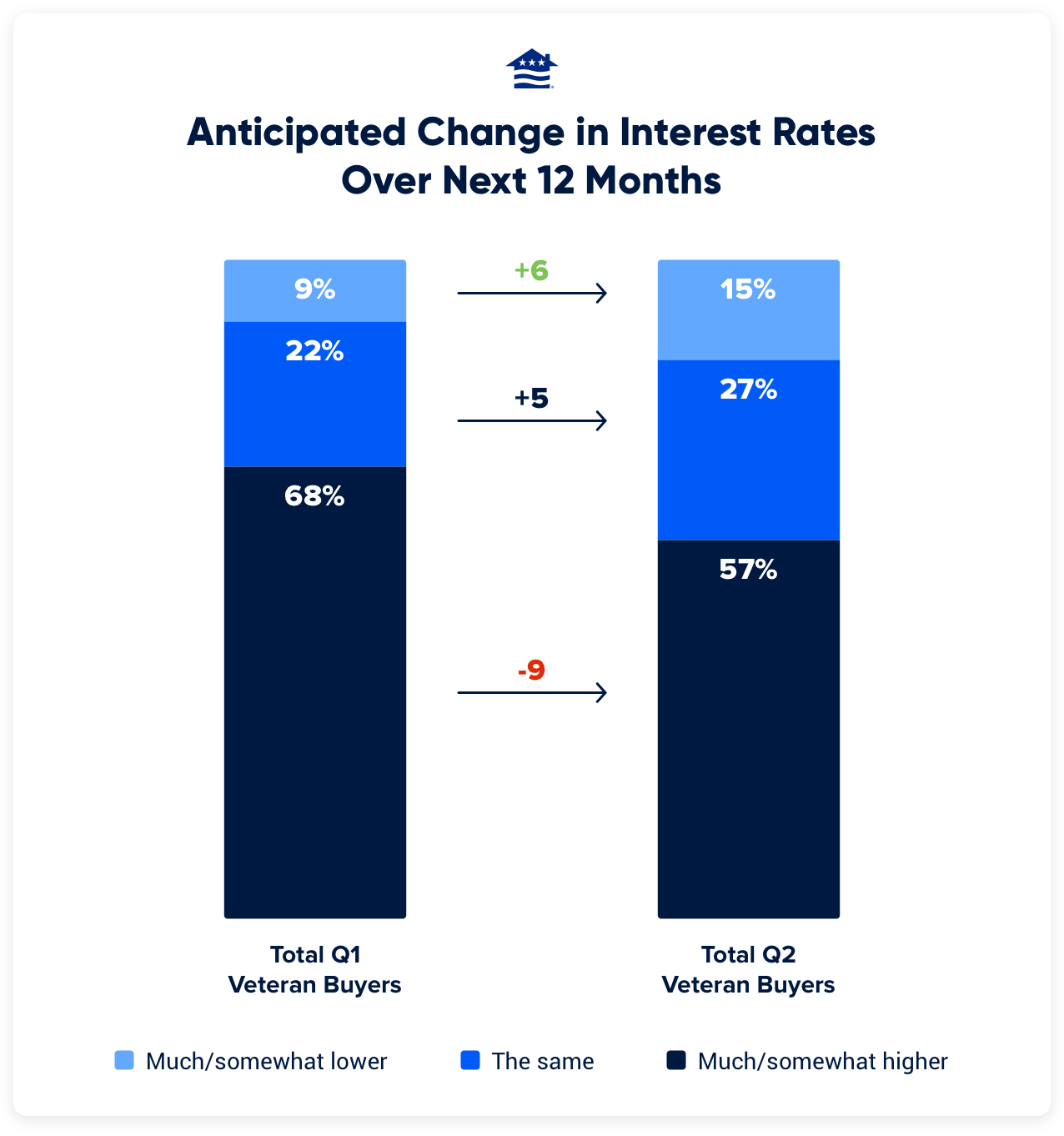
When it comes to financing a home, VA loans have become increasingly popular amongst military veterans and active-duty service members. Offering competitive interest rates and flexible terms, VA loans provide a unique opportunity for those who have served our country to achieve the dream of homeownership. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the details of VA loan rates today and provide you with all the information you need to make an informed decision.
Understanding VA Loans
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers VA loans to eligible veterans, service members, and their surviving spouses. These loans are backed by the government, allowing lenders to offer more favorable terms and interest rates compared to conventional loans. To qualify for a VA loan, individuals must meet certain eligibility criteria, including military service requirements and creditworthiness.
Eligibility Criteria
VA loans are available to veterans who have served a minimum period of time, typically 90 consecutive days during wartime or 181 consecutive days during peacetime. National Guard and Reserve members may also be eligible after serving for six years. Additionally, surviving spouses of veterans who died in service or as a result of a service-connected disability may qualify for VA loans.
Benefits of VA Loans
One of the primary benefits of VA loans is the absence of a down payment requirement. This makes homeownership more accessible for veterans who may not have significant savings. VA loans also do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI), which can save borrowers a substantial amount of money each month. Additionally, VA loans offer competitive interest rates and more flexible qualification requirements compared to conventional loans.
Requirements and Advantages
VA loans have specific requirements, including a satisfactory credit score, stable income, and a Certificate of Eligibility (COE) issued by the VA. The COE confirms an individual’s eligibility for a VA loan based on their military service record. One of the advantages of VA loans is the ability to finance up to 100% of the home’s value, eliminating the need for a down payment. This can be a significant advantage for veterans who may not have substantial savings.
Factors Affecting VA Loan Rates
VA loan rates can vary based on several factors. Understanding these factors can help borrowers secure the most favorable rates possible.
Credit Score
One of the primary factors that influence VA loan rates is the borrower’s credit score. Lenders typically offer better rates to borrowers with higher credit scores, as they are considered less risky. It is essential for borrowers to maintain a good credit score by making timely payments, reducing outstanding debts, and avoiding new credit inquiries before applying for a VA loan.
Loan Term
The term of the loan also affects the interest rate. Generally, shorter loan terms, such as 15 years, have lower interest rates compared to longer terms, such as 30 years. Borrowers should evaluate their financial goals and choose a loan term that aligns with their budget and long-term plans.
Loan Amount
The loan amount can impact the interest rate as well. Larger loan amounts may result in slightly higher rates compared to smaller loan amounts. Borrowers should carefully consider their borrowing needs and evaluate the impact of the loan amount on their monthly payments and overall cost of borrowing.
Market Conditions and Economic Factors
VA loan rates are also influenced by market conditions and economic factors. Factors such as inflation, the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy, and the overall state of the economy can impact interest rates. Borrowers should stay informed about current market trends and consult with lenders to make strategic decisions regarding the timing of their loan application.
Finding the Best VA Loan Rates
Securing the best VA loan rates requires some research and careful consideration. Here are some steps to help borrowers find the most favorable rates:
Shop Around
It is crucial for borrowers to compare rates and offers from different lenders. Each lender may have slightly different rates and fees, so shopping around can help borrowers identify the most competitive options.
Compare Loan Estimates
Borrowers should request loan estimates from multiple lenders. These estimates provide detailed information about the loan terms, including the interest rate, closing costs, and any other fees. Comparing loan estimates allows borrowers to make an informed decision based on the overall cost of borrowing.
Negotiate for Better Rates
Borrowers should not be afraid to negotiate with lenders. If a borrower has a strong credit history and a stable financial situation, they may be able to negotiate for better rates or reduced fees. It is essential to advocate for the best possible terms and explore all available options.
Improve Credit Score
As mentioned earlier, credit score plays a significant role in determining loan rates. Borrowers can improve their credit score by paying bills on time, reducing credit card balances, and disputing any errors on their credit report. Taking steps to improve creditworthiness can lead to more favorable loan rates.
Fixed vs. Adjustable VA Loan Rates
When obtaining a VA loan, borrowers have the option to choose between fixed or adjustable interest rates. Each option has its advantages and considerations.
Fixed Interest Rates
With a fixed interest rate, the rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan. This provides borrowers with stability and predictability, as their monthly payments will not change. Fixed rates are an excellent choice for borrowers who prefer consistency and want to avoid any surprises in their budget.
Adjustable Interest Rates
Adjustable interest rates, also known as adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs), offer an initial fixed-rate period followed by periodic adjustments based on market conditions. The initial fixed-rate period is typically lower than the prevailing fixed rates, making ARMs an attractive option for borrowers who plan to sell or refinance their home before the rate adjustments occur.
Considerations
When choosing between fixed and adjustable rates, borrowers should consider their financial goals, risk tolerance, and future plans. Fixed rates provide stability, while adjustable rates offer potential savings in the short term. It is essential to carefully evaluate the pros and cons of each option and consult with a mortgage professional to make an informed decision.
VA Loan Rates vs. Conventional Loan Rates
Comparing VA loan rates with conventional loan rates can help borrowers understand the advantages and disadvantages of each option.
Interest Rate Trends
VA loan rates are generally more competitive than conventional loan rates. The government backing and reduced risk for lenders allow VA loans to offer lower interest rates compared to conventional loans. Borrowers should monitor interest rate trends and take advantage of favorable market conditions.
Qualification Requirements
Conventional loans typically have stricter qualification requirements compared to VA loans. VA loans have more flexible credit score requirements and may allow for a higher debt-to-income ratio. This can make VA loans more accessible for borrowers who may not meet the stringent criteria set by conventional loan lenders.
Down Payment
Conventional loans often require a significant down payment, typically around 20% of the home’s purchase price. In contrast, VA loans do not require a down payment, making homeownership more accessible for veterans who may not have substantial savings.
Private Mortgage Insurance
Conventional loans may require private mortgage insurance (PMI) if the borrower’s down payment is less than 20% of the home’s value. PMI adds an additional cost to the monthly mortgage payment. VA loans, on the other hand, do not require PMI, potentially saving borrowers a significant amount over the life of the loan.
Loan Limits
VA loans have specific loan limits set by the VA based on the county in which the property is located. These limits determine the maximum amount a borrower can borrow without having to make a down payment. Conventional loans may have higher loan limits, allowing borrowers to finance more expensive properties.
Considerations
When comparing VA loan rates with conventional loan rates, borrowers should consider their specific financial situation, long-term goals, and eligibility. Consulting with a mortgage professional can help borrowers evaluate the benefits and drawbacks of each option and choose the most suitable loan for their needs.
VA Loan Refinancing Rates
Refinancing a VA loan can be a smart financial move for borrowers who want to take advantage of lower interest rates or change the terms of their loan.
Lower Interest Rates
One of the primary reasons borrowers refinance their VA loans is to secure a lower interest rate. If interest rates have decreased since the initial loan was obtained, refinancing can help borrowers reduce their monthly mortgage payments and save money over the life of the loan.
Cash-Out Refinancing
Cash-out refinancing allows borrowers to tap into their home’s equity by refinancing for a higher amount than the current loan balance. This can be an attractive option for borrowers who need funds for home improvements, debt consolidation, or other financial needs.
Streamline Refinancing
Streamline refinancing, also known as the Interest Rate Reduction Refinance Loan (IRRRL), is a simplifiedprocess that allows borrowers to refinance their existing VA loan with minimal documentation and paperwork. Streamline refinancing is typically used to lower the interest rate or switch from an adjustable-rate mortgage to a fixed-rate mortgage.
Considerations
Before refinancing a VA loan, borrowers should carefully evaluate their financial goals and consider the costs associated with refinancing. It is essential to compare the potential savings from refinancing with the closing costs and fees involved. Additionally, borrowers should be aware of any potential impact on their credit score and eligibility for future VA loans.
VA Loan Rates and Mortgage Insurance
VA loans do not require private mortgage insurance (PMI), which is typically required for conventional loans with a down payment of less than 20%. However, VA loans have the VA funding fee, which is a one-time fee paid at closing.
VA Funding Fee
The VA funding fee is a fee charged by the VA to help fund the VA loan program. The fee is a percentage of the loan amount and varies based on factors such as the borrower’s military category, down payment amount, and whether it is the borrower’s first VA loan or subsequent use. The funding fee can be paid upfront or rolled into the loan amount.
Impact on Loan Rate
The VA funding fee does not directly impact the interest rate of the loan. However, it does affect the overall cost of borrowing. Borrowers should consider the funding fee when comparing loan options and calculating the total cost of homeownership.
Waiving the Funding Fee
In some cases, borrowers may be eligible to have the VA funding fee waived. This typically applies to veterans with a service-related disability. Waiving the funding fee can result in significant savings, but borrowers should consult with the VA and their lenders to determine if they qualify for this exemption.
VA Loan Rates and Closing Costs
Closing costs are fees and expenses associated with finalizing a mortgage loan. While VA loans generally have lower closing costs compared to conventional loans, borrowers should still be aware of the potential costs involved.
Types of Closing Costs
Common closing costs include loan origination fees, appraisal fees, title insurance, attorney fees, and prepaid items such as property taxes and homeowners insurance. These costs can vary depending on factors such as the loan amount, property location, and lender’s policies.
Negotiating and Reducing Costs
Borrowers have the option to negotiate certain closing costs with the lender. Some fees may be waived or reduced, potentially resulting in savings. It is essential for borrowers to review the Loan Estimate provided by the lender and understand each itemized cost. Comparing offers from different lenders can also help borrowers identify the most cost-effective option.
Rolling Closing Costs into the Loan
Borrowers can choose to roll the closing costs into the loan amount instead of paying them upfront. This allows borrowers to finance the closing costs, but it increases the overall loan balance and may slightly increase the interest rate. Borrowers should carefully evaluate the long-term cost implications before choosing this option.
VA Loan Rates and VA Loan Limits
VA loan limits determine the maximum amount a borrower can borrow without making a down payment. These limits are set by the VA and vary based on the county in which the property is located.
Impact on Loan Rate
VA loan limits do not directly impact the interest rate of the loan. However, they can affect the borrower’s borrowing capacity. Borrowers who need to borrow more than the VA loan limits may need to make a down payment for the excess amount or explore other financing options.
Maximizing Loan Amount within Limits
Borrowers can maximize their loan amount within the VA loan limits by utilizing their entitlement and considering factors such as the down payment and their creditworthiness. Understanding the VA loan limits and working with a knowledgeable lender can help borrowers optimize their borrowing potential.
The Future of VA Loan Rates
Like all interest rates, VA loan rates are subject to change based on various factors. While it is impossible to predict the future with certainty, certain trends and indicators can provide insights into the direction of VA loan rates.
Economic Factors
The state of the economy, inflation rates, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policies can influence interest rates. Economic growth and stability generally lead to higher interest rates, while economic downturns may result in lower rates. Staying informed about economic indicators and market trends can help borrowers anticipate potential changes in VA loan rates.
Government Policies
Government policies and regulations can also impact VA loan rates. Changes in legislation or regulations related to the VA loan program can have an indirect effect on interest rates. Monitoring any proposed or implemented policy changes can provide insights into potential shifts in VA loan rates.
Market Conditions
Market conditions, including supply and demand dynamics and investor sentiment, can influence interest rates. Borrowers should stay informed about market trends, such as the demand for mortgage-backed securities, which can impact VA loan rates.
Armed with a comprehensive understanding of VA loan rates today, you are well-equipped to navigate the world of home financing. By leveraging the benefits of VA loans and keeping a close eye on the current market, you can secure the most favorable rates and achieve your homeownership goals. Remember to consult with VA loan experts and compare offers from different lenders to ensure you make the most informed decision possible. VA loans provide an excellent opportunity to unlock the door to your dream home with competitive rates tailored to those who have dutifully served our nation.