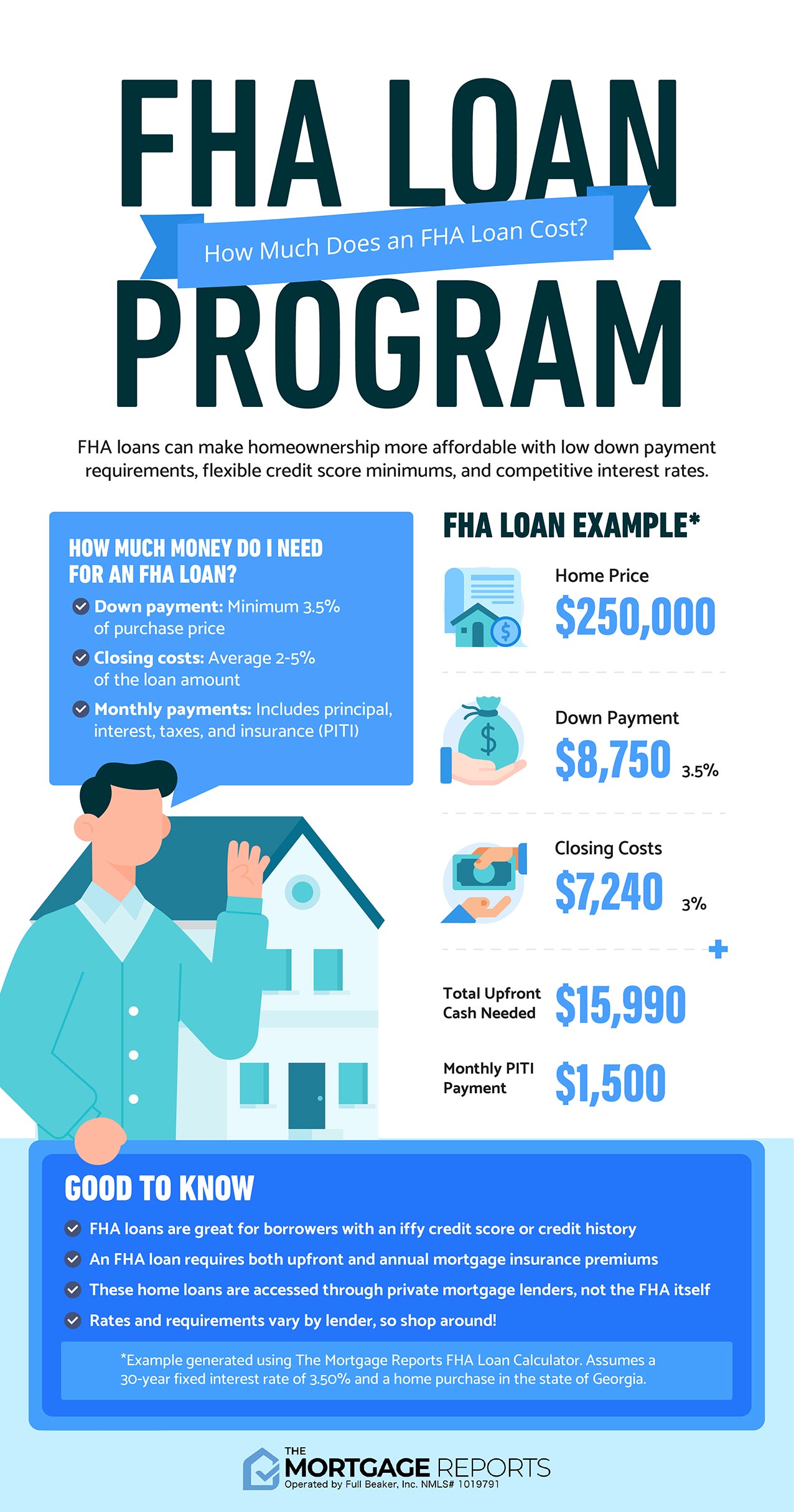
Are you dreaming of owning your own home but struggling to save up for a down payment? Look no further than the FHA home loan program. Designed to make homeownership more accessible, this government-backed loan has helped millions of Americans achieve their dreams of buying a home. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about FHA home loans, from eligibility requirements to the application process, and even tips for maximizing your chances of approval. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of FHA home loans!
What is an FHA Home Loan?
When it comes to financing your dream home, FHA home loans can be a game-changer. Unlike conventional mortgages, FHA loans are insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), a government agency established in 1934 to support affordable housing initiatives. The primary goal of the FHA is to make homeownership more accessible by providing lenders with insurance against potential borrower default.
One of the key advantages of FHA loans is the relaxed eligibility criteria compared to conventional mortgages. While a traditional lender may require a substantial down payment, typically around 20% of the home’s purchase price, FHA loans offer more flexible options. With an FHA loan, you may only need a down payment as low as 3.5% of the purchase price, making homeownership more attainable for those with limited savings.
Subheading 1: Benefits of FHA Home Loans
• Low Down Payment: The ability to purchase a home with a minimal down payment is one of the most significant advantages of an FHA loan. This feature makes homeownership more accessible to individuals who may not have substantial savings.
• Lenient Credit Requirements: FHA loans are known for their more relaxed credit score requirements. Borrowers with a credit score as low as 580 may still be eligible for an FHA loan, whereas conventional mortgages often require higher credit scores.
• Flexible Debt-to-Income Ratio: FHA loans are more forgiving when it comes to debt-to-income ratios, which measure your monthly debt payments compared to your gross monthly income. This flexibility can be beneficial for borrowers with existing debts, such as student loans or credit card payments.
• Availability of Rehabilitation Loans: FHA 203(k) loans provide financing for both the purchase of a home and its renovation costs. This option is ideal for individuals who wish to buy a fixer-upper and make necessary repairs or upgrades.
Subheading 2: How FHA Loans Differ from Conventional Mortgages
While both FHA loans and conventional mortgages serve the purpose of financing a home purchase, there are some key differences between the two. Understanding these distinctions can help you decide which option is better suited to your needs.
• Mortgage Insurance: One significant difference is that FHA loans require mortgage insurance premiums (MIP) throughout the life of the loan. This insurance protects the lender in case of borrower default. In contrast, conventional mortgages may require private mortgage insurance (PMI) until you reach a certain level of equity in the home.
• Credit Score Requirements: FHA loans tend to be more lenient when it comes to credit score requirements. As mentioned earlier, borrowers with a credit score as low as 580 may still qualify for an FHA loan. In contrast, conventional mortgages may require higher credit scores, often above 620.
• Down Payment: FHA loans offer the advantage of a lower down payment requirement compared to conventional mortgages. With an FHA loan, you may be able to put down as little as 3.5% of the purchase price, whereas conventional mortgages typically require a down payment of at least 5% to 20%.
• Property Standards: FHA loans have specific property standards that must be met for the loan to be approved. These standards ensure that the property is safe and habitable. In contrast, conventional mortgages generally have fewer property requirements, allowing for a broader range of property options.
Eligibility Requirements
Before diving into the FHA loan application process, it’s crucial to understand the eligibility requirements. While FHA loans are known for their more lenient criteria compared to conventional mortgages, certain conditions must still be met to qualify.
Subheading 1: Credit Score
Your credit score plays a significant role in determining your eligibility for an FHA loan. While there is no strict minimum credit score requirement, most lenders prefer borrowers with a score of at least 580. With a credit score below 580, you may still be eligible for an FHA loan, but you may need to provide a larger down payment.
Subheading 2: Employment and Income
Lenders want to ensure that you have a stable source of income to repay the loan. Generally, you must have a steady employment history for the past two years. Self-employed individuals may be eligible if they can provide sufficient documentation, such as tax returns and profit/loss statements.
Furthermore, your income should be sufficient to cover your monthly mortgage payments, including taxes, insurance, and other debts. The FHA sets debt-to-income ratio limits, typically around 43%. This means that your total monthly debts should not exceed 43% of your gross monthly income.
Subheading 3: Residency and Legal Status
To qualify for an FHA loan, you must be a legal resident of the United States and have a valid Social Security number. Non-resident aliens are generally not eligible for FHA loans, although there may be exceptions for certain categories, such as those married to U.S. citizens.
Subheading 4: Property Requirements
In addition to borrower eligibility, FHA loans have specific property requirements that must be met. These standards ensure that the property is safe, habitable, and structurally sound. Some of these requirements include:
• The property must be your primary residence.
• The home must meet minimum property standards set by the FHA.
• The property must have adequate heating, cooling, and ventilation systems.
• The home must have a sufficient number of bedrooms and bathrooms for its intended occupancy.
• The property must have a safe and potable water supply.
The Application Process
Now that you understand the eligibility requirements, it’s time to delve into the FHA loan application process. Applying for an FHA loan involves several steps, from gathering the necessary documents to submitting your application to an FHA-approved lender.
Subheading 1: Preparing Your Documents
Before starting the application process, gather all the necessary documents to streamline the process. These documents typically include:
• Proof of identification (e.g., driver’s license, passport).
• Social Security number.
• Proof of income (e.g., pay stubs, W-2 forms, tax returns).
• Employment history for the past two years.
• Bank statements and other financial documents.
• Proof of residency (e.g., utility bills, rental agreements).
• Documentation of any existing debts (e.g., student loans, credit card statements).
• Purchase agreement or contract for the intended property.
Subheading 2: Finding an FHA-Approved Lender
As FHA loans are insured by the government, you’ll need to work with an FHA-approved lender to apply for the loan. These lenders are authorized to provide FHA loans and have experience navigating the FHA loan process. Research and compare different lenders to find the one that best suits your needs.
Once you’ve chosen a lender, contact them to initiate the application process. They will guide you through the necessary steps and paperwork required to move forward.
Subheading 3: Completing the Loan Application
With your documents in order and an FHA-approved lender by your side, it’s time to complete the loan application. This involves providing detailed information about your financial situation, employment history, and the property you wish to purchase.
The loan application will include questions about your income, assets, debts, and credit history. Be prepared to provide accurate information and ensure that you disclose any relevant details, as misrepresenting information on your application can lead to severe consequences.
Subheading 4: Underwriting and Loan Approval
Once you’ve submitted your loan application, the lender will begin the underwriting process. During this stage, the lender evaluates your financial information, verifies the property’s value, and assesses your eligibility for an FHA loan.
The underwriter will review your credit score, employment history, income, and debt-to-income ratio. They will also order an appraisal to determine the fair market value of the property.
If your application meets the necessary criteria and the property meets FHA standards, your loan will be approved. You will then receive a commitment letter outlining the terms and conditions of the loan.
Subheading 5: Closing the Loan
The final step in the application process is closing the loan. This involves reviewing and signing the loan documents, paying any required closing costs, and officially transferring ownership of the property.
During the closing, you will sign the mortgage note, which is a legal document outlining yourobligations and responsibilities as the borrower. You will also sign the deed of trust, which secures the loan with the property as collateral. Additionally, you will be provided with a closing disclosure, which details the final terms of the loan, including interest rate, monthly payments, and any fees or costs associated with the loan.
Once all the documents are signed and the necessary funds are exchanged, the loan is considered closed, and you become the proud owner of your new home. Congratulations!
FHA Loan Types
When it comes to FHA home loans, there are various types to choose from based on your specific needs and circumstances. Understanding the different loan types can help you make an informed decision about which one is the best fit for you.
1. Fixed-Rate FHA Loans
A fixed-rate FHA loan is the most common type of FHA loan. With this loan, the interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan, providing stability and predictability in your monthly mortgage payments. This option is ideal for borrowers who prefer a consistent payment amount over the long term.
Summary: Fixed-rate FHA loans offer stability with a consistent interest rate and predictable monthly payments.
2. Adjustable-Rate FHA Loans
Adjustable-rate FHA loans, also known as FHA ARM loans, have interest rates that may fluctuate over time. These loans typically start with a lower initial interest rate for an introductory period, often 3, 5, 7, or 10 years. After the introductory period, the interest rate adjusts periodically based on market conditions. This type of loan is suitable for borrowers who plan to sell or refinance their home before the introductory period ends.
Summary: Adjustable-rate FHA loans offer lower initial interest rates and are ideal for borrowers who plan to sell or refinance their home before the interest rate adjusts.
3. FHA 203(k) Rehabilitation Loans
If you’re purchasing a fixer-upper or planning significant renovations for your current home, an FHA 203(k) rehabilitation loan can be a great option. This loan provides financing for both the purchase of the property and the cost of necessary repairs or upgrades. With an FHA 203(k) loan, you can finance the renovation expenses into your mortgage, simplifying the financing process.
Summary: FHA 203(k) rehabilitation loans provide financing for the purchase of a home and renovation costs, making them ideal for those looking to buy a fixer-upper.
4. FHA Streamline Refinance Loans
If you already have an FHA loan and want to take advantage of lower interest rates or reduce your monthly payments, an FHA streamline refinance loan may be an excellent option. This type of loan allows you to refinance your existing FHA loan with minimal documentation and paperwork. The streamline refinance process is designed to be quick and straightforward, making it an attractive choice for borrowers seeking to save money on their mortgage.
Summary: FHA streamline refinance loans allow borrowers with existing FHA loans to refinance with minimal documentation and paperwork.
5. Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM) Loans
If you’re interested in making energy-efficient improvements to your home, an FHA Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM) loan can help finance those upgrades. This loan allows you to borrow additional funds on top of your FHA loan amount to make energy-efficient improvements, such as installing solar panels, upgrading insulation, or replacing old appliances. The energy-efficient upgrades can help reduce your home’s environmental impact and save you money on utility bills.
Summary: FHA Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM) loans provide additional funding to finance energy-efficient improvements to your home.
FHA Loan Limits
When considering an FHA loan, it’s essential to understand the loan limits set by the Federal Housing Administration. These limits determine the maximum amount you can borrow through an FHA loan and vary by county and property type.
The FHA loan limits are based on the median home prices in a particular area. The limits are updated annually to reflect changes in housing markets and ensure that the program remains accessible to borrowers across different regions.
Factors Influencing FHA Loan Limits
Several factors influence FHA loan limits, including:
1. Median Home Prices
The primary factor is the median home prices in a specific area. Higher-priced areas typically have higher loan limits, while lower-priced areas have lower loan limits.
Summary: FHA loan limits are influenced by the median home prices in a particular area.
2. Property Type
The type of property you’re purchasing also affects the loan limits. FHA loan limits may differ for single-family homes, duplexes, triplexes, and four-unit properties.
Summary: FHA loan limits can vary based on the type of property you’re purchasing.
3. High-Cost Areas
In areas where housing costs are significantly higher than the national average, FHA loan limits are adjusted to accommodate the higher expenses. This allows borrowers in high-cost areas to access FHA loans without being restricted by lower loan limits.
Summary: FHA loan limits are adjusted in high-cost areas to accommodate the higher housing expenses.
Recent Updates on FHA Loan Limits
It’s important to stay informed about recent updates on FHA loan limits, as they can impact your borrowing capabilities. The FHA regularly reviews and adjusts loan limits based on changes in housing markets. By keeping up with these updates, you can ensure that you have accurate information when planning your home purchase.
Summary: Stay updated on recent FHA loan limit adjustments to understand how they may affect your borrowing capabilities.
FHA Mortgage Insurance
Mortgage insurance is a crucial aspect of FHA loans and plays a significant role in making homeownership more accessible. FHA loans require borrowers to pay mortgage insurance premiums (MIP) throughout the life of the loan. This insurance protects lenders against potential borrower default, allowing them to offer more favorable terms and lower down payment requirements.
Subheading 1: Upfront Mortgage Insurance Premium (UFMIP)
When you obtain an FHA loan, you’ll be required to pay an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP). This premium is a one-time payment made at closing and is usually a percentage of the loan amount. The UFMIP can be paid upfront or rolled into the loan amount.
The UFMIP payment helps fund the FHA insurance program and provides immediate coverage for the lender in case of borrower default. The amount of UFMIP you pay depends on the loan term, loan amount, and the loan-to-value ratio (LTV).
Subheading 2: Annual Mortgage Insurance Premium (MIP)
In addition to the upfront mortgage insurance premium, FHA loans require borrowers to pay an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP). The MIP is paid as part of your monthly mortgage payment and is calculated based on the loan amount, loan term, and loan-to-value ratio.
The MIP payment is divided into monthly installments, which are added to your mortgage payment. The exact amount of the MIP depends on the size of your loan, the loan term, and the loan-to-value ratio.
Summary: FHA loans require borrowers to pay an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) at closing and an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP) as part of their monthly mortgage payment.
Pros and Cons of FHA Loans
As with any type of mortgage, FHA loans have their advantages and potential drawbacks. Understanding the pros and cons can help you make an informed decision about whether an FHA loan is the right choice for you.
Pros of FHA Loans
• Low Down Payment: One of the most significant advantages of FHA loans is the low down payment requirement, which can be as low as 3.5% of the purchase price. This makes homeownership more accessible, especially for first-time buyers or those with limited savings.
• Lenient Credit Requirements: FHA loans are known for their more relaxed credit score requirements compared to conventional mortgages. Borrowers with lower credit scores may still be eligible for an FHA loan, providing an opportunity to improve their creditworthiness while becoming homeowners.
• Competitive Interest Rates: FHA loans often offer competitive interest rates, making them an attractive option for borrowers looking for affordable monthly payments.
• Flexible Debt-to-Income Ratio: FHA loans have more flexible debt-to-income ratio requirements compared to conventional mortgages. This allows borrowers with existing debts to still qualify for an FHA loan as long as their debt-to-income ratio falls within acceptable limits.
• Assumable Loans: FHA loans are assumable, meaning that if you decide to sell your home, the buyer can take over your existing FHA loan. This feature can be advantageous in a rising interest rate environment, as the assumption of a lower-rate FHA loan can be an attractive selling point.
Summary: FHA loans offer low down payment options, lenient credit requirements, competitive interest rates, flexible debt-to-income ratios, and the ability to assume the loan.
Cons of FHA Loans
• Mortgage Insurance Premiums
One potential drawback of FHA loans is the requirement to pay mortgage insurance premiums (MIP). Both the upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) and the annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP) add to the overall cost of the loan. This additional cost can increase your monthly mortgage payment.
• Loan Limits: FHA loan limits vary by county and property type, which means there may be restrictions on the loan amount you can qualify for in certain areas. If you’re looking to purchase a higher-priced property, you may need to explore alternative loan options.
• Property Standards: FHA loans have specific property standards that must be met for the loan to be approved. These standards ensure that the property is safe, habitable, and structurally sound. While these standards are in place to protect both the borrower and the lender, they may limit the range of available properties.
• Lifetime Mortgage Insurance Premiums: Unlike conventional mortgages that allow borrowers to cancel private mortgage insurance (PMI) once they reach a certain level of equity, FHA loans require mortgage insurance premiums for the life of the loan. This means you will continue to pay MIP even after reaching 20% equity in your home.
• Additional Documentation: FHA loans may require more documentation during the application process compared to conventional mortgages. This can include providing detailed financial statements, past tax returns, and additional verification of income and employment history.
Summary: Potential drawbacks of FHA loans include the requirement to pay mortgage insurance premiums, loan limits that may restrict borrowing capabilities, specific property standards, lifetime mortgage insurance premiums, and additional documentation during the application process.
Tips for Increasing Your Chances of Approval
If you’re considering an FHA loan, there are steps you can take to increase your chances of approval and secure the loan you need. By following these tips, you can improve your eligibility and demonstrate your financial readiness to lenders.
1. Improve Your Credit Score
While FHA loans have more lenient credit score requirements, a higher credit score can still work in your favor. Take steps to improve your credit score by paying bills on time, reducing your credit card balances, and addressing any errors on your credit report. By demonstrating responsible financial habits, you can boost your creditworthiness and increase your chances of approval.
2. Reduce Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Lenders carefully evaluate your debt-to-income ratio to assess your ability to manage mortgage payments. If your debt-to-income ratio is high, consider paying down existing debts or consolidating them to improve your financial profile. This will show lenders that you have sufficient income to handle your mortgage payments along with other financial obligations.
3. Save for a Larger Down Payment
While FHA loans offer low down payment options, saving for a larger down payment can help strengthen your loan application. A larger down payment reduces the loan amount and shows lenders that you have the financial discipline and stability to save for a significant upfront payment.
4. Maintain Stable Employment
Stable employment history is an essential factor in FHA loan eligibility. Lenders prefer borrowers who have a steady employment record, ideally with the same employer for at least two years. Avoid making significant job changes or career shifts during the loan application process, as this may raise concerns for lenders.
5. Gather and Organize Your Documentation
Having all the necessary documentation prepared and organized can streamline the loan application process. Gather documents such as pay stubs, W-2 forms, bank statements, and tax returns. Providing complete and accurate documentation will help lenders assess your financial situation more efficiently.
6. Work with an Experienced FHA-Approved Lender
Choosing the right lender can make a significant difference in your FHA loan experience. Look for an FHA-approved lender with experience in FHA loans. An experienced lender can guide you through the application process, answer your questions, and provide valuable insights based on their expertise.
7. Seek Pre-Approval
Consider getting pre-approved for an FHA loan before starting your home search. Pre-approval provides a clearer understanding of your budget and strengthens your position as a serious buyer. It also gives you an advantage in competitive housing markets, as sellers may prioritize offers from pre-approved buyers.
8. Be Patient and Persistent
Securing an FHA loan may require patience and persistence. If your initial application is not approved, don’t be discouraged. Take the time to address any issues or concerns raised by the lender, such as improving your credit score or reducing your debt. With determination and perseverance, you can increase your chances of approval.
9. Stay Informed about FHA Guidelines
FHA guidelines and requirements may change over time. Stay informed about any updates or changes to ensure you meet all the necessary criteria. Keeping up with the latest guidelines will help you navigate the FHA loan process more effectively.
10. Consult with an FHA-Approved Housing Counselor
If you have questions or concerns about the FHA loan process, consider consulting with an FHA-approved housing counselor. These professionals can provide guidance, answer your questions, and help you navigate the complexities of FHA loans. Their expertise can be invaluable in ensuring a smooth and successful loan application.
Common Misconceptions about FHA Loans
As with any financial product, there are common misconceptions surrounding FHA loans. It’s essential to separate fact from fiction to make informed decisions about your homeownership journey. Let’s debunk some of the most prevalent misconceptions:
Misconception 1: FHA Loans Have High Interest Rates
Contrary to popular belief, FHA loans do not necessarily have higher interest rates than conventional mortgages. The interest rate you qualify for depends on various factors, such as your credit score, financial profile, and current market conditions. By shopping around and comparing rates from different lenders, you can find competitive interest rates for your FHA loan.
Misconception 2: FHA Loans Limit Property Choices
While FHA loans have property requirements, they do not necessarily limit your choices. FHA-approved properties include single-family homes, condominiums, multi-unit properties, and even some manufactured homes. As long as the property meets FHA standards, you have a wide range of options to choose from.
Misconception 3: FHA Loans Are Only for First-Time Homebuyers
While FHA loans are popular among first-time homebuyers, they are not exclusive to this group. Anyone who meets the eligibility requirements can qualify for an FHA loan, regardless of whether they’ve owned a home before. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or a repeat buyer, FHA loans can be a viable financing option.
Misconception 4: FHA Loans Are Difficult to Qualify For
While there are eligibility requirements for FHA loans, they are generally more lenient compared to conventional mortgages. FHA loans are designed to make homeownership more accessible, particularly for borrowers with lower credit scores or limited down payment funds. By meeting the necessary criteria and providing the required documentation, you can increase your chances of qualifying for an FHA loan.
Misconception 5: FHA Loans Cannot Be Used for Investment Properties
While FHA loans are primarily intended for owner-occupied properties, there are exceptions that allow for financing investment properties. FHA 203(k) loans, for example, can be used to purchase a property and finance necessary renovations for both owner-occupied and investment purposes. It’s important to consult with an FHA-approved lender to explore your options if you’re considering an investment property.
Alternatives to FHA Home Loans
While FHA loans are a popular choice for many homebuyers, they may not be the best fit for everyone. If an FHA loan doesn’t meet your specific requirements or preferences, there are alternative housing loan options to consider:
1. Conventional Mortgages
Conventional mortgages are loans that are not backed by a government agency like the FHA. These loans typically have stricter eligibility criteria and may require higher down payments and higher credit scores. However, conventional mortgages offer more flexibility in terms of loan amounts, property types, and mortgage insurance requirements.
Summary: Conventional mortgages have stricter eligibility criteria but offer more flexibility in terms of loan amounts, property types, and mortgage insurance requirements.
2. VA Loans
VA loans are available to eligible veterans, active-duty military personnel, and their spouses. These loans are guaranteed by the Department of Veterans Affairs and offer competitive interest rates, low or no down payment options, and flexible eligibility requirements. VA loans can be an excellent alternative for those who have served in the military.
Summary: VA loans are available to eligible veterans, active-duty military personnel, and their spouses, offering competitive rates, low or no down payment options, and flexible eligibility requirements.
3. USDA Loans
USDA loans are designed to assist low- to moderate-income borrowers in rural areas. These loans are backed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture and offer low or no down payment options, competitive interest rates, and flexible credit requirements. USDA loans can be an attractive choice for those looking to purchase a home in eligible rural areas.
Summary: USDA loans are available to low- to moderate-income borrowers in eligiblerural areas, offering low or no down payment options, competitive interest rates, and flexible credit requirements.
4. State and Local Homebuyer Programs
Many states and local governments offer homebuyer assistance programs to help individuals and families achieve homeownership. These programs may provide down payment assistance, closing cost assistance, or other forms of financial support. Research the programs available in your area to see if you qualify for additional assistance.
Summary: State and local homebuyer programs provide assistance, such as down payment or closing cost support, to help individuals and families achieve homeownership.
5. Private Mortgage Financing
Private mortgage financing involves obtaining a loan from a private lender or individual rather than a traditional financial institution. These lenders may have different eligibility criteria and loan terms compared to FHA or conventional mortgages. Private mortgage financing can be an option for borrowers who do not meet the requirements of other loan programs.
Summary: Private mortgage financing involves obtaining a loan from a private lender or individual and may be an option for borrowers who do not meet the requirements of other loan programs.
6. Down Payment Assistance Programs
Down payment assistance programs can provide financial aid to help cover the upfront costs of homeownership. These programs can be offered by state or local governments, non-profit organizations, or even employers. They may provide grants, loans, or other forms of assistance to help bridge the gap between your available funds and the required down payment.
Summary: Down payment assistance programs offer financial aid to help cover the upfront costs of homeownership and can be provided by various organizations or employers.
7. Rent-to-Own Programs
Rent-to-own programs allow you to rent a property with the option to purchase it at a later date. A portion of your monthly rent goes toward building equity in the property, which can be used as a down payment when you decide to buy. Rent-to-own programs can be beneficial for those who need more time to save for a down payment or improve their credit score.
Summary: Rent-to-own programs allow you to rent a property with the option to purchase it later, helping you build equity and potentially use it as a down payment.
8. Co-Borrowing or Co-Signing
If you’re unable to qualify for a loan on your own, you may consider co-borrowing or having a co-signer. Co-borrowing involves applying for the loan with another person, such as a spouse or family member, who shares the responsibility of repaying the loan. A co-signer, on the other hand, agrees to take on the financial responsibility if you default on the loan. Both options can help strengthen your loan application.
Summary: Co-borrowing or having a co-signer can be options if you’re unable to qualify for a loan on your own, as it helps strengthen your loan application.
9. Save for a Larger Down Payment
If none of the available loan options meet your needs, you may choose to save for a larger down payment. By saving a significant amount upfront, you may have access to more loan options or be able to secure a conventional mortgage with lower interest rates and no mortgage insurance requirements.
Summary: Saving for a larger down payment can provide access to more loan options and potentially eliminate the need for mortgage insurance.
10. Explore Other Financing Options
Lastly, consider exploring other financing options available in your area or through specialized programs. These may include grants, employer-assisted housing programs, or other creative financing solutions. Research and consult with local housing agencies or financial institutions to explore all the possibilities.
Summary: Explore other financing options, such as grants or employer-assisted housing programs, to find additional assistance or creative financing solutions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, FHA home loans provide an accessible pathway to homeownership for many Americans. With their low down payment options, lenient credit requirements, and attractive interest rates, FHA loans have helped countless individuals and families achieve their dreams of owning a home. By understanding the ins and outs of FHA loans, including eligibility requirements, the application process, and available loan types, you can make an informed decision about whether this affordable housing solution is right for you.
Remember to consult with an experienced FHA-approved lender who can guide you through the process and help you secure the loan that best suits your needs. By following the tips for increasing your chances of approval and addressing any misconceptions, you can navigate the FHA loan process with confidence. If an FHA loan doesn’t meet your specific requirements, explore alternative loan options or assistance programs available in your area. With determination, preparation, and the right resources, you’ll be one step closer to turning your homeownership dreams into reality!